Optical Diffusers
Optical diffusers are precision-engineered components designed to scatter light uniformly, enabling consistent illumination and accurate calibration in optical systems. Widely used in aerospace, medical imaging, and remote sensing, these diffusers ensure optimal light distribution while maintaining superior performance under demanding conditions, including extreme temperatures and radiation exposure.
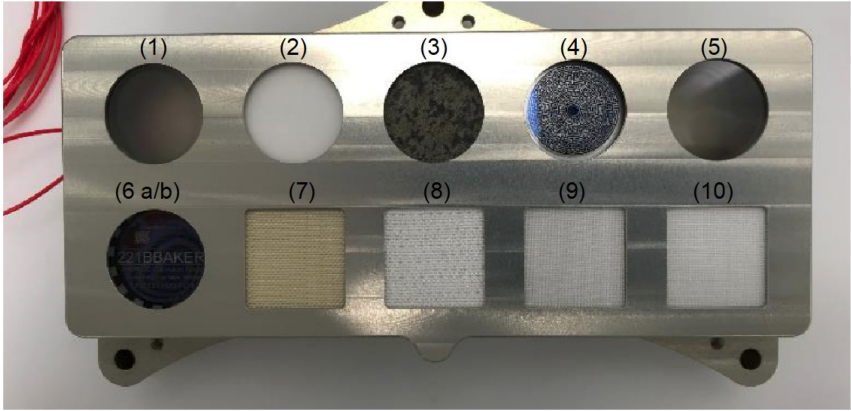
Firebird Optics specializes in manufacturing high-performance optical diffusers tailored to meet the needs of advanced optical systems. Crafted using Diffusil from IQS GmbH, the highest-grade fused silica material in the world, our diffusers deliver exceptional thermal stability, uniform light scattering, and resistance to radiation and contamination. These features make them indispensable for critical applications like Earth observation, aerospace instrumentation, and high-precision laboratory environments.
Holographic Diffusers
Holographic Diffusers
Specialized optical components known as holographic diffusers are employed to scatter and evenly disperse light in a controlled manner. They create intricate interference patterns, transforming incoming light waves into a diffused output that spreads out uniformly. Holographic diffusers have widespread applications in lighting systems, display technologies, and imaging setups, where controlling light diffusion is crucial for achieving specific visual effects or improving overall optical performance.
Holographic Diffusers
The Best Diffuser for High Transmission
| Material: Polycarbonate | Coating: Uncoated |
|---|---|
| Transmittance > 85% | Damage Threshold, By Design: 0.22 J/cm2 @ 1064nm, 10ns (typical) |
| Operating Temperature (°C): -30 to +100 (Maximum of 240 Hours) |
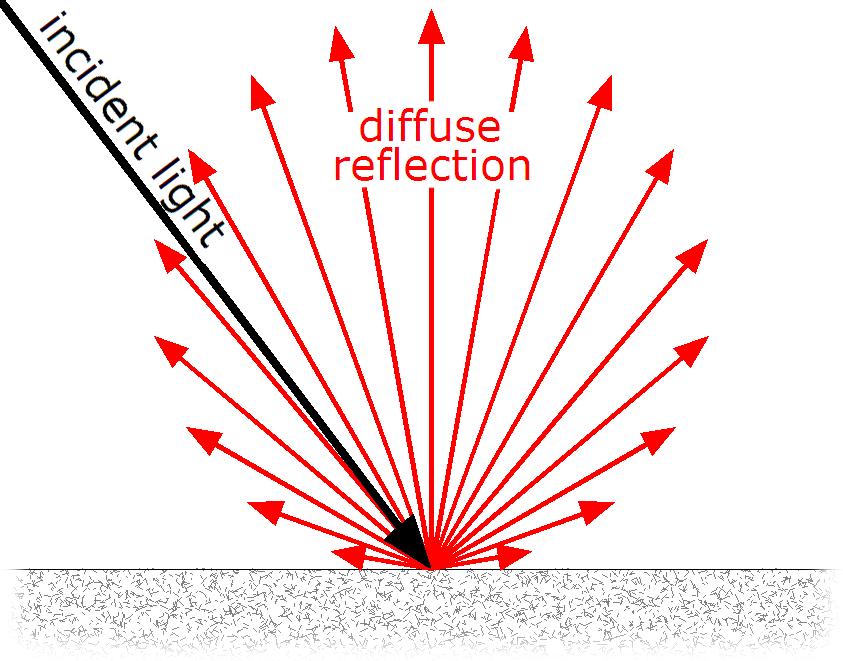
The primary function of holographic diffusers is to break up and homogenize incoming light, transforming it into a more even and uniform distribution of intensity and direction. This is particularly useful in applications where even illumination or controlled scattering of light is necessary as it increases transmission efficiency to greater than 90%. The manufacturing process for holographic diffusers typically involves recording an interference pattern on a photosensitive material using laser light.
This pattern is created by the interaction of a reference beam and an object beam, which contains the information about the desired light distribution. After the recording, the material is developed, resulting in a surface with microstructures that produce the desired diffraction pattern. The microstructures on the holographic diffuser's surface act as tiny diffraction gratings.
The term "holographic" refers to the use of holography, a technique that records and reconstructs the wavefront of light to create three-dimensional images. In the context of holographic diffusers, holography is utilized to fabricate a surface structure that possesses specific diffraction properties, allowing the diffuser to manipulate light in a desired way. When light passes through the diffuser, it gets diffracted by these microstructures, leading to the redistribution of light into various angles and directions.
The specific design of the diffuser determines the angular distribution and intensity of the scattered light. Holographic diffusers have several advantages over traditional diffusers, such as superior light control, high efficiency, and the ability to create complex and precise light distributions. These properties make them suitable for a wide range of applications, including display backlighting, head-up displays, photography diffusers, and light shaping in various optical systems.
Why use a Holographic Diffuser?
Medical Imaging: In medical imaging devices, holographic diffusers can help improve image quality by reducing artifacts and optimizing the distribution of light within the imaging system.
3D Sensing: Holographic diffusers can be used in depth-sensing applications, like time-of-flight cameras, structured light systems, or LiDAR, to improve the accuracy and reliability of distance measurements.
Scientific Research: Holographic diffusers are valuable tools in various scientific experiments and research projects, where controlled and uniform light scattering is required.
Beam Shaping: Holographic diffusers can shape light beams into specific patterns, such as Gaussian-like distributions or uniform profiles. This makes them valuable in laser applications, such as laser beam homogenization or reshaping for specific optical setups.
Optical Metrology: Holographic diffusers are useful in optical metrology and testing applications. They can be employed as calibration targets or to generate known and controlled light patterns for testing cameras, lenses, and other optical components.
Because of holographic diffusers’ versatility and control over light distribution, making them valuable components in a wide range of applications in optics, photonics, displays, imaging, and beyond.