Optical Windows
Optical windows are transparent components made of materials like glass or crystal that are used to protect and control the flow of light in optical systems. IR windows and optics for use in FTIR Spectroscopy and CO2 lasers. This includes discs, rectangular plates and various other geometries.
In various fields, optical windows serve many purposes. They act as protective barriers, shielding sensitive optical components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and contaminants. Additionally, they enable the transmission of light while minimizing distortion, reflection, and absorption, thus maintaining the integrity of the optical system.
Optical windows are employed in a wide range of applications, including scientific research, industrial manufacturing, aerospace, defense, and telecommunications. They are utilized in optical instruments like cameras, microscopes, telescopes, lasers, and sensors. By providing a stable optical interface, optical windows facilitate accurate measurements, imaging, and analysis of light, enabling advancements in numerous fields.
Optical windows come in many shapes and sizes but a major factor is their material. The types of materials that an optical window is constructed from dictate the wavelengths (measured in nm) that they can view. In IR It is extremely important that selecting the right material is done to avoid many a headache and a waste of money and time.
If you are having choice fatigue and are getting overwhelmed by all the options please check out our optical window guide.
Barium Fluoride (BaF2) Windows

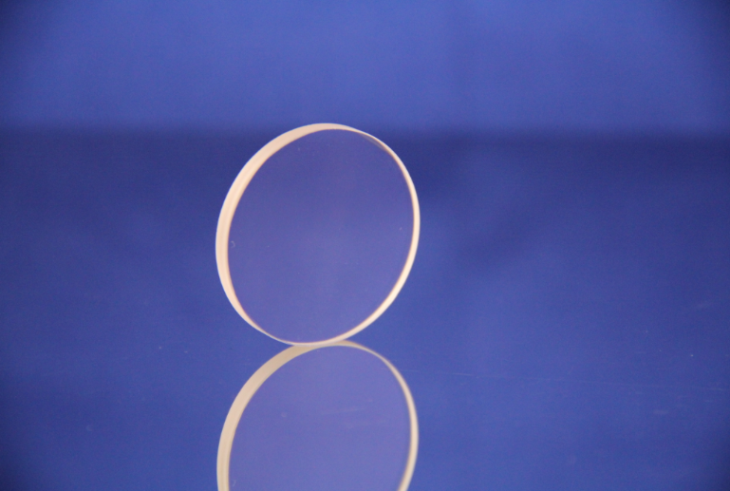



Barium Fluoride (BaF2) Windows
Barium Fluoride or BaF2 can be used in many applications due to its wide transmission range that goes from the deep UV to the far infrared range. BaF2's main standout is its resistance to high-energy radiation and low index of refraction of 1.48, which makes it so that AR coatings are unnecessary. While, these windows can but used in temperatures up to 800ºC, it must be in a dry environment or else the moisture will damage its transmission properties in the UV range.
Typically, BaF2 is used to detect X-rays, gamma rays and other high energy particles as it is a fast scintillator.
Firebird provides these in several uncoated stock configurations but can provide customized and coated to your specifications.
Barium Fluoride (BaF2) Window Specs:
| Wavelength range: 200-12µm | Coating: Uncoated |
|---|---|
| Diameter tolerance: ±0.1mm | Surface Quality: 60/40 |
| Thickness tolerance: ±0.2mm | Paralellism: <3 arc minute |
| Clear Aperture: 90% | Density: 3.18g/cm3 | Melting point: 1360ºC | Young's Modulus: (GPa): 53 | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 18.1 x 10-6/°C | Knoop Hardness: 82kg/mm2 |
Barium Fluoride Window Overview:
BaF2 (Barium Fluoride) windows are optical components made from a crystalline material with the chemical formula BaF2. They have a number of properties that make them useful for a wide range of applications, including high transparency in the visible and ultraviolet (UV) spectrums, good hardness and scratch resistance, high chemical stability, and good thermal stability.
In terms of optical properties, BaF2 windows have a high refractive index, which makes them ideal for use in optical systems that require high levels of light gathering. They are also highly transparent in the UV spectrum, which makes them ideal for use in UV optical systems. Additionally, BaF2 windows are highly resistant to UV degradation, making them ideal for use in applications that require exposure to UV radiation.
BaF2 windows are also highly resistant to chemical attack, making them ideal for use in harsh environment applications that require exposure to harsh chemicals. They are also capable of withstanding high temperatures, which makes them ideal for use in high-temperature environments.
In terms of dimensional stability, BaF2 windows exhibit minimal change in their physical dimensions when exposed to changes in temperature and pressure, making them ideal for use in high-precision applications. They are also transparent in the infrared (IR) spectrum, making them ideal for use in IR optical systems.
Material Characteristics of Barium Fluoride Windows:
Optical Transparency: BaF2 has high transmission in the visible and ultraviolet (UV) spectrums, making it ideal for use in a wide range of optical applications.
Hardness: BaF2 is relatively hard and scratch-resistant, which makes it ideal for use in applications where durability and scratch resistance are important.
Chemical Stability: BaF2 is highly resistant to chemical attack, making it ideal for use in applications that require exposure to harsh chemicals.
Thermal stability: BaF2 has good thermal stability and is capable of withstanding high temperatures, making it ideal for use in high-temperature environments.
UV resistance: BaF2 is highly resistant to UV degradation, making it ideal for use in applications that require exposure to UV radiation.
Dimensional stability: BaF2 exhibits minimal change in its physical dimensions when exposed to changes in temperature and pressure, making it ideal for use in high-precision applications.
Infrared (IR) transparency: BaF2 is also transparent in the infrared (IR) spectrum, making it ideal for use in IR optical systems.
Overall, Baf2 is a versatile optical material with a range of properties that make it ideal for use in a wide range of applications, including UV and IR optical systems, high-precision optical instruments, and harsh environment applications.
7 Reasons to Use BaF2 in your Optical Setup:
BaF2 (Barium Fluoride) is used over other infrared (IR) materials in certain applications due to its specific properties and performance advantages. Some reasons for using BaF2 over other IR materials include:
High IR transparency: BaF2 has a high transmission in the IR spectrum, making it ideal for use in IR optical systems.
High UV transmission: BaF2 also has high transmission in the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum, making it ideal for use in UV optical systems.
Good thermal stability: BaF2 has good thermal stability and is capable of withstanding high temperatures, making it ideal for use in high-temperature environments.
Chemical stability: BaF2 is highly resistant to chemical attack, making it ideal for use in applications that require exposure to harsh chemicals.
Hardness: BaF2 is relatively hard and scratch-resistant, making it ideal for use in applications where durability and scratch resistance are important.
Dimensional stability: BaF2 exhibits minimal change in its physical dimensions when exposed to changes in temperature and pressure, making it ideal for use in high-precision applications.
Availability: BaF2 is readily available and can be produced in large quantities, making it a cost-effective solution for many applications.
Overall, BaF2's high IR transparency, UV transmission, thermal stability, chemical stability, hardness, dimensional stability, and availability make it a suitable material for certain applications over other IR materials. The specific requirements of a particular application will determine whether Baf2 or another material is the best choice.Barium Fluoride (BaF2) Specs:
Firebird Optics’ BaF2 windows enabled Purdue University to conduct groundbreaking research on acoustic streaming and heat transfer. These precision-engineered optics facilitated high-resolution thermal imaging and flow visualization, driving innovations in aerospace and thermal management systems.
KBr windows are a little different to clean as they are hygroscopic. Let’s delve into this topic to learn some tricks of the trade!
Are your optics covered in schmutz? Let’s discuss how to clean them up and how to mitigate this in the future.







Finding the right optical window can be an exercise in choice fatigue. Let us help!