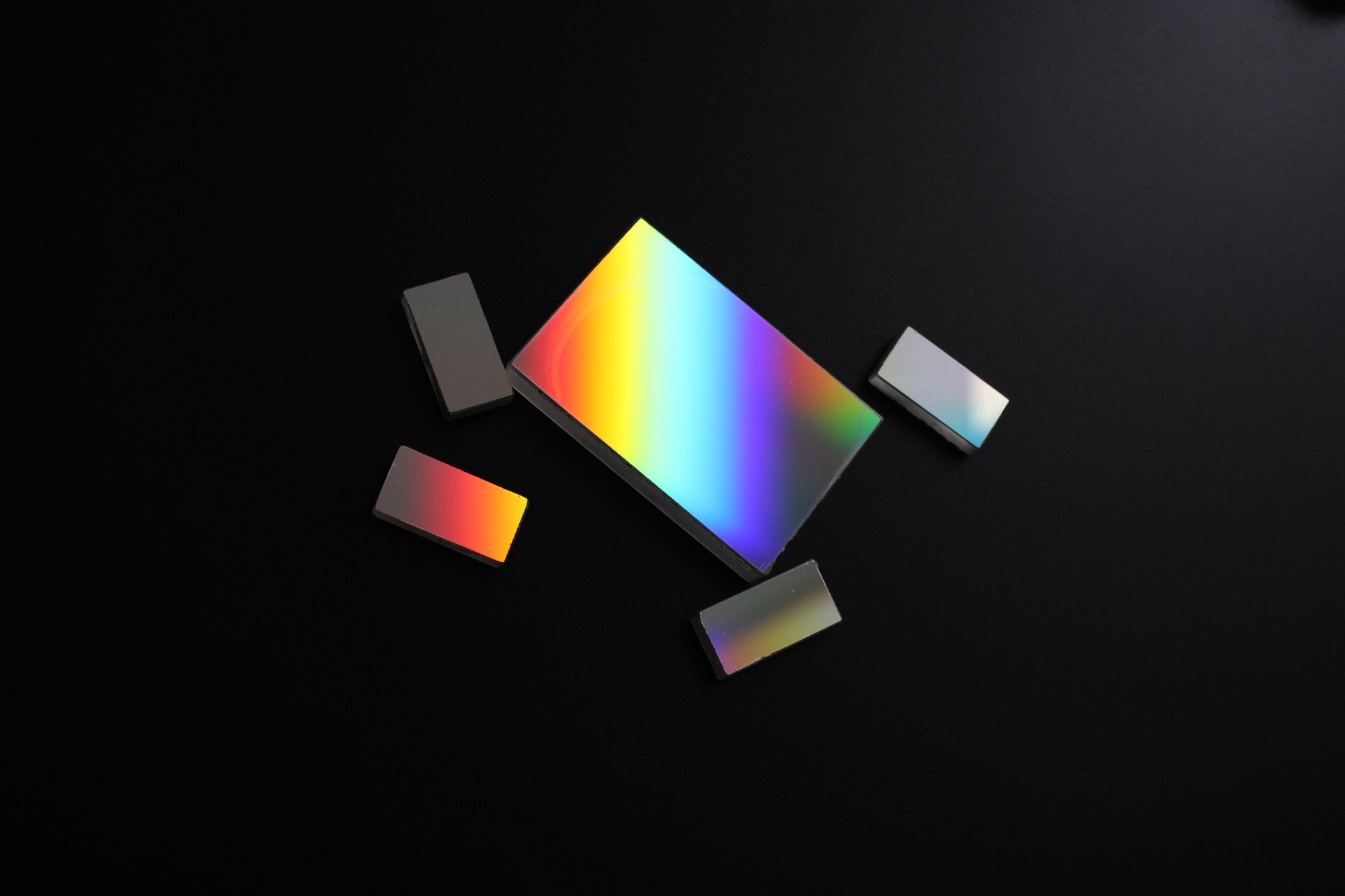
Structure and Working Principle of Transmission Gratings
Transmission gratings consist of a substrate made of glass or another transparent material. A series of equally spaced lines are then etched onto the surface of the substrate, with the spacing between the lines determining the diffraction pattern. The lines are generally made from a reflective material such as aluminum, which makes them opaque.
When light passes through a transmission grating, it diffracts into various orders, which depend on the spacing between the lines. The diffraction angle is determined by the wavelength of the incident light and the grating period. The transmitted light then forms a pattern of bright spots, known as the diffraction pattern.
Applications of Transmission Gratings
One of the most common applications of transmission gratings is in spectroscopy. By using a transmission grating, it is possible to separate the different wavelengths of light in a spectrum. This technique is used extensively in the fields of chemistry and physics, allowing researchers to identify and analyze the chemical composition of various substances.
Transmission gratings are also used in telecommunications. They are used to separate the various wavelengths of light in a fiber optic cable, allowing multiple signals to be sent simultaneously. This technique, known as wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), is used extensively in modern communication systems.
Finally, transmission gratings are used in laser systems. They are used to control the direction and intensity of the laser beam, allowing it to be focused or redirected as needed. They are also used in interferometry, which is a technique used to measure very small distances and motions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Transmission Gratings
One of the primary advantages of transmission gratings is their ability to diffract light over a wide range of wavelengths. This makes them useful in a variety of applications, from spectroscopy to telecommunications.
However, transmission gratings also have some disadvantages. They can be challenging to manufacture, requiring precise control over the grating period and line spacing. Additionally, the diffraction pattern produced by transmission gratings can be complex, making it difficult to analyze and interpret.
Conclusion
Transmission gratings are essential optical devices that are used in a wide range of applications, from spectroscopy to telecommunications. By splitting light into its constituent wavelengths, they allow researchers to analyze and understand the physical and chemical properties of materials. While transmission gratings can be challenging to manufacture and analyze, their versatility and usefulness make them an essential tool in modern science and technology.